There are now more than 8 billion people in the world. Since the beginning of this year, 90 million children have been born, which is more than twice the number of people living in Poland. The long-term projections of the United Nations can be terrifying, because by the year 2100 there will be as many as 11 billion people on Earth. Are we able to house these people somewhere, or are we at risk of overcrowding?
It turns out that we are not so much, on the contrary, because the Earth looks like a desolate planet. Why? Because half of the world’s population lives on only 1% of the Earth’s surface. Moreover, half of the population lives in Asia, more precisely, in only 6 countries, where 46 percent of the world’s population lives.
The dispersion of the population is constantly diminishing in favor of the expansion of cities. Some of them deserve to be called megacities. Tokyo, the capital of Japan, and its suburbs are home to more than 40 million people, which is more than the whole of Poland.
In the future, urban giants will become even larger. Its area is increasing much more slowly than the population density. This means that more and more people live in a smaller and smaller area. Why do so many people cram into such a small space? Humans are herd mammals. Cities give them the chance to develop, do well, and connect, but they also expose them to noise, smog, and lack of freedom.
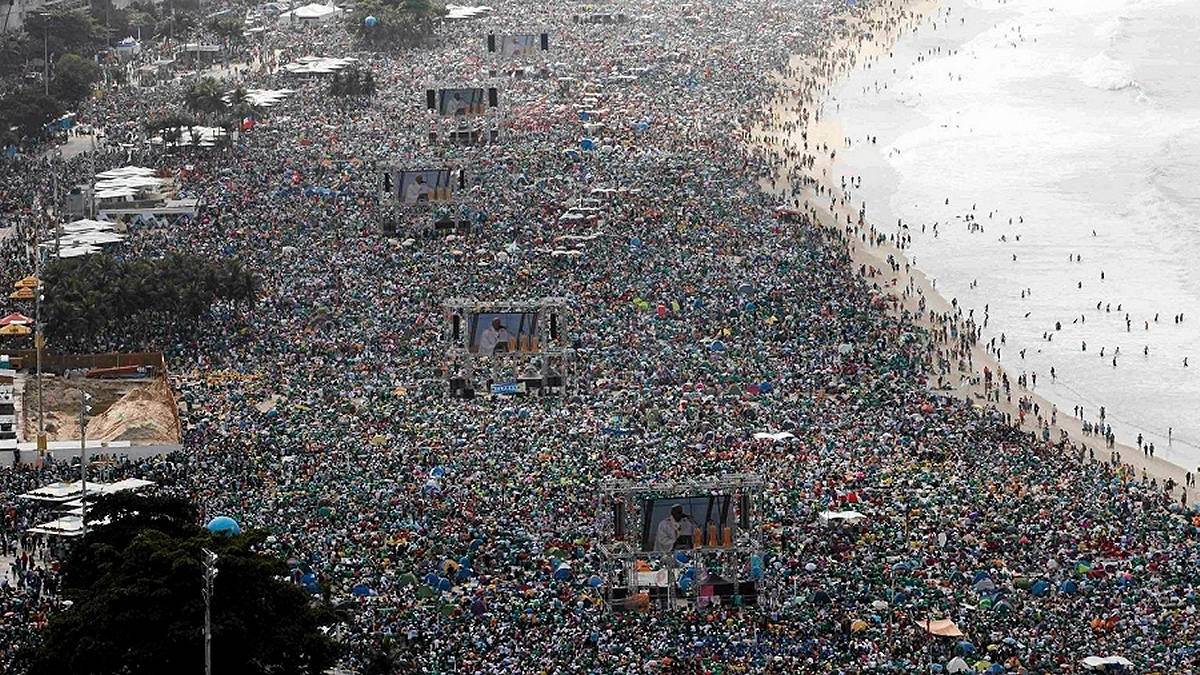 International Youth Day at Copacabana Beach in Rio de Janeiro. picture. Paul Whitaker.
International Youth Day at Copacabana Beach in Rio de Janeiro. picture. Paul Whitaker.
On the island of Java, Indonesia, the population reaches 140 million, although it is three times less than Poland. It is as if 420 million people live in Poland, ten times more than today.
Max Galka, a publicist fascinated by statistics and cartography, made a very interesting map of the world, which he divided into 28 million cells, each measuring 5 by 5 kilometres. Yellow marks places where half of the world’s population lives in high concentrations. The other half lives in great scattering on a black surface.
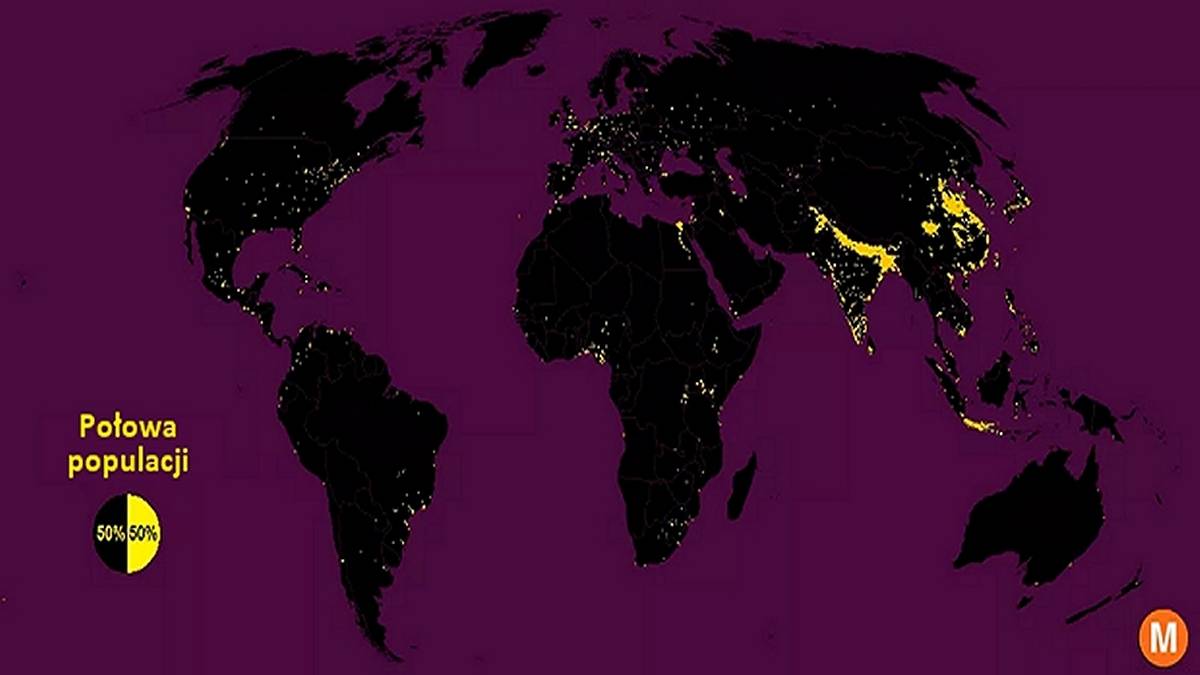 Half of the population is marked in yellow and the other half in black. Data: Max Galka.
Half of the population is marked in yellow and the other half in black. Data: Max Galka.
The map showed the two most densely populated regions of our planet. One covers a strip of fertile soil in northern India at the foot of the Himalayas, the other covers eastern China.
And when we say that China and India are the most populous countries in the world, with a total of 2.5 billion people, we are referring to the vast areas of these countries, which are among the largest in the world. However, in reality, the vast majority of the population lives in only a small part of these countries.
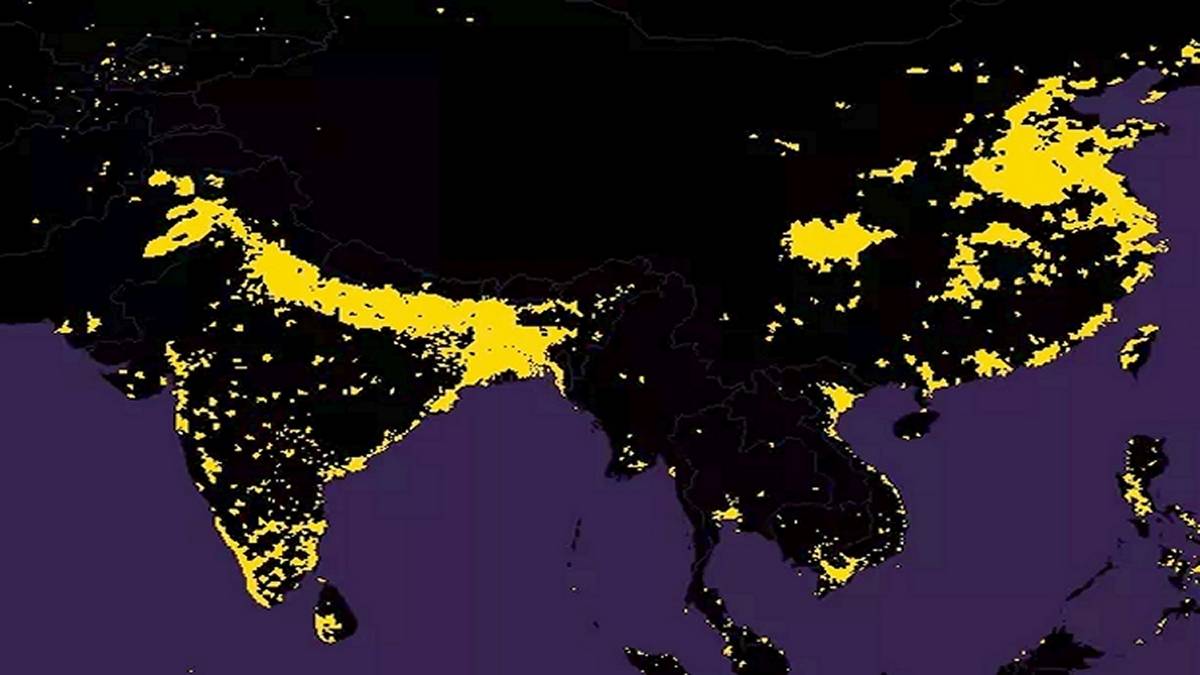 The most densely populated regions on the planet are in India and China. Data: Max Galka.
The most densely populated regions on the planet are in India and China. Data: Max Galka.
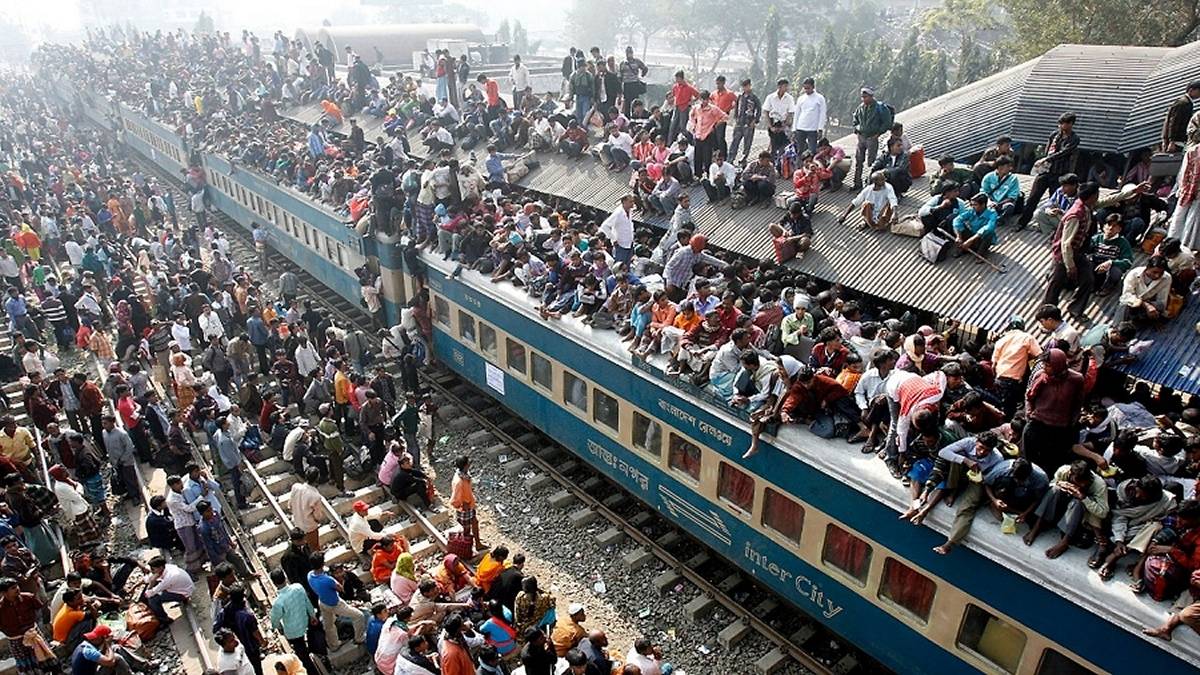
The rest of the areas are inhabited or completely uninhabited. This is evidenced by the invention of Thomas Edison nearly 140 years ago. The lamp began to illuminate the places where the man was. Today electricity reveals our presence on the new night map of the world (look here) and created by NASA in recent years.
Most of us live in temperate and tropical regions. The farther you go to the poles, the smaller the population, and it looks like it will stay that way into the future, unless we face some drastic climate change.
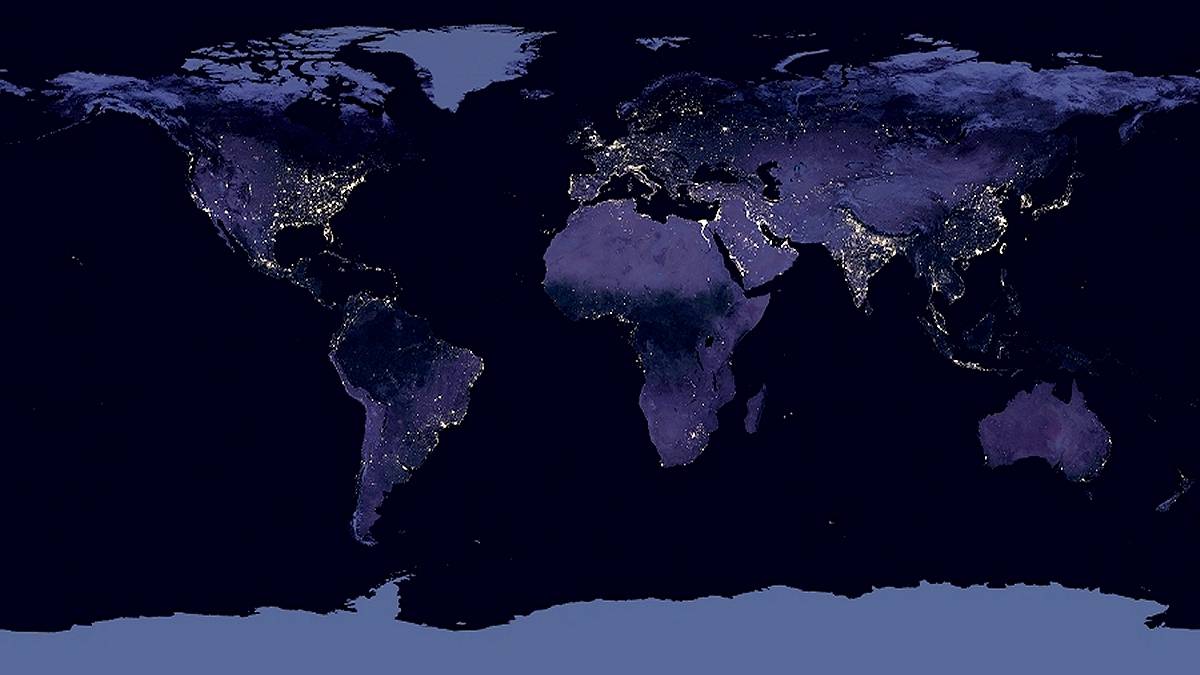 Earth at night in 2016 photo. NASA / NOAA / Suomi NBB / IOSDIS / GSFC.
Earth at night in 2016 photo. NASA / NOAA / Suomi NBB / IOSDIS / GSFC.
United Nations projections leave no room for doubt that the next three billion people who will be born by the end of this century can only be accommodated in Africa alone. It is currently the least inhabitable continent in the world by population. Africa is, and will continue to be, the fastest-populating place on earth.
In Asia, that is, in India or China, the population will only increase rapidly until the middle of this century, and then it will decline. Slow population growth will occur in the Americas.
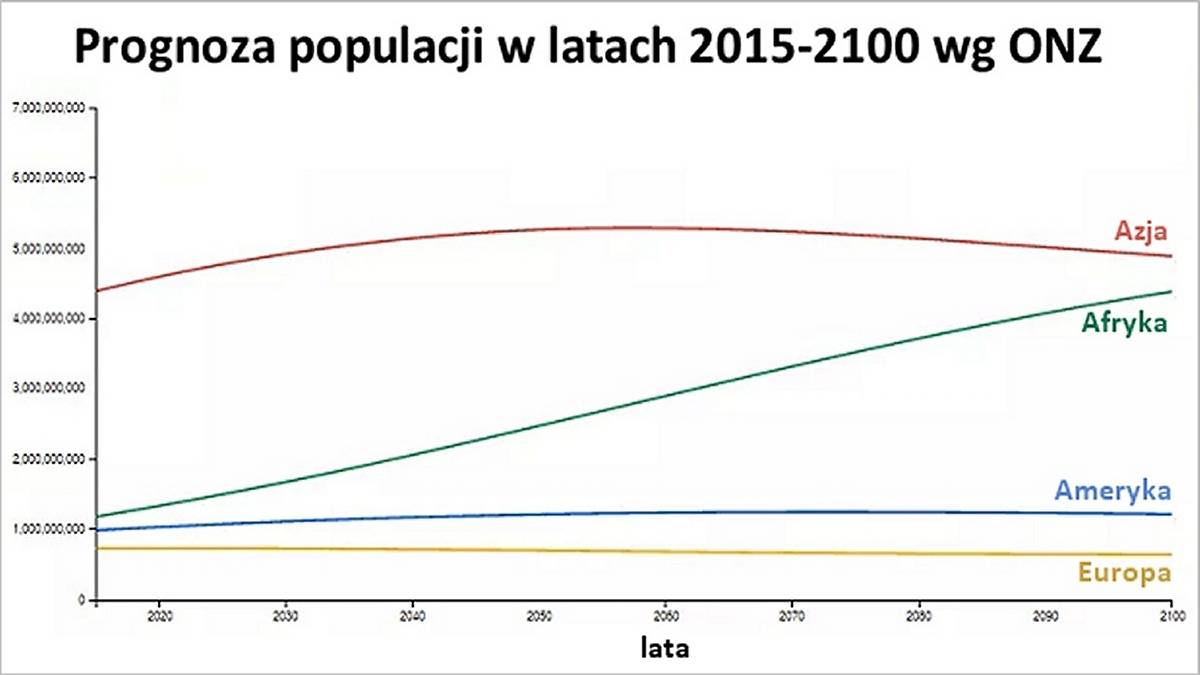 Population projections for individual continents in the period 2010–2105. Data: United Nations/Max Galka.
Population projections for individual continents in the period 2010–2105. Data: United Nations/Max Galka.
Meanwhile, Europe may face extinction as the population continues to decline. However, this may change, as climate change and geopolitical situations may have a massive impact on populations in the future, which will lead to massive migrations of peoples, which are just beginning to happen before our eyes.
And in Western European countries, where the standard of living is high and a lot of money is spent on social issues, migrants from Africa or Asia can find shelter, displacing the original population over time.
Although the Earth is still not very densely populated in terms of the area we occupy, due to the problems of food production, overfishing, soil and air pollution, and the use of mineral resources, it is.
Source: MojePogoda.pl / United Nations / NASA / Max Galka.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.


![You can buy such clothes for adults and children today on the market at ul. Durak in Rzeszow [ZDJĘCIA]](https://d-art.ppstatic.pl/kadry/k/r/1/90/9c/64f42cfc6e299_o_original.jpg)