They write about their idea in the pagesOpen Engineering. The authors of the post used dust, potato starch, and small amounts of salt. In this way, concrete was created with twice the usual strength. What else do we know about StarCrete?
Read also: Mars with holes like Swiss cheese. These structures tell us a lot about the Red Planet
First of all, given the limited capabilities of transporting Martian dust to Earth, StarCrete is unlikely to be a tempting option for local builders. However, it can work great, for example, as a material for creating shelters on the Red Planet.
To be precise, members of the research team used the equivalent of Martian soil. Until now, it has not been possible to deliver its samples to our planet. And while that should change soon (due to a mission to collect samples and send them back to Earth), the science world will probably have a million better ideas for using such valuable materials.
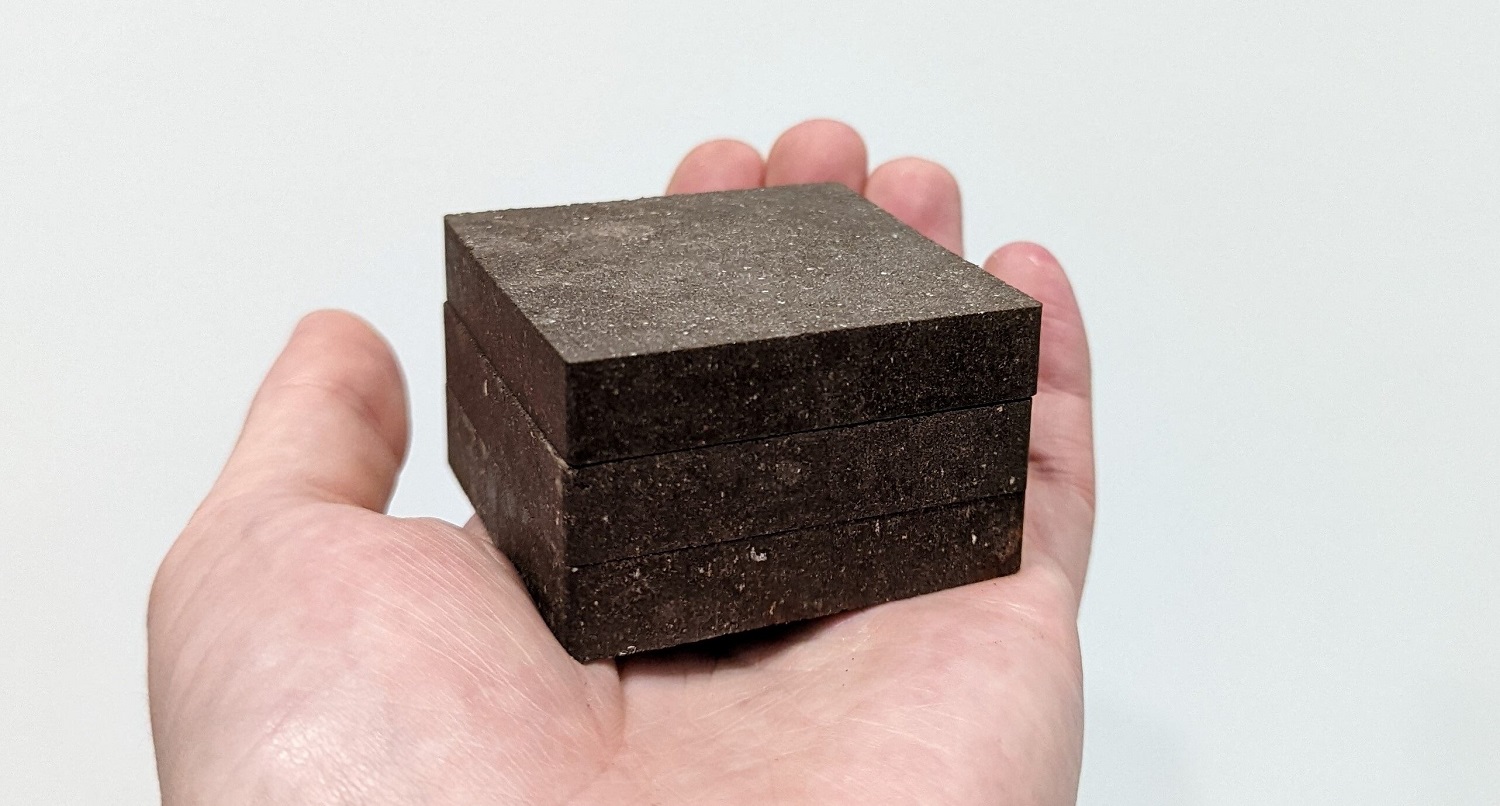
Star concrete is made from moon or martian dust
But let’s go back to our concreteness. The equivalent of Mars dust was mixed with potato starch and a pinch of salt. Starch can act as a bonding agent, and strength tests have shown that StarCrete can withstand pressures of up to 72 MPa. This is more than twice the 32 MPa value for “normal” concrete.
Interestingly, the scientists did not limit themselves to just one variable. They also tested the second option, which included lunar dust as part of the star concrete. Here the final result was even more impressive, since we’re talking about 91 MPa. Calculations show that a 25kg bag of partially dehydrated potatoes contains enough starch to produce approximately half a ton of StarCrete. This amount should be enough to make more than 200 bricks.
Read also: They wanted to produce oxygen on the moon, but they made another breakthrough. Even more important
This material is still too little for the construction of the whole building, but the idea itself seems to be the most important. The researchers also noted that magnesium chloride, which is easily obtainable on the Red Planet, enhanced StarCrete’s durability.
The possibility of using local resources to build shelters on the Moon or Mars will be very important if humanity is serious about colonizing these facilities. However, before the astronauts can move from words to deeds, they must be patient. More testing of new materials is needed to ensure that they can be produced on a sufficiently large scale. And even if the average inhabitant of Earth does not have direct contact with Starcrete, we as humans can gain a lot by exploring other objects in the solar system.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.