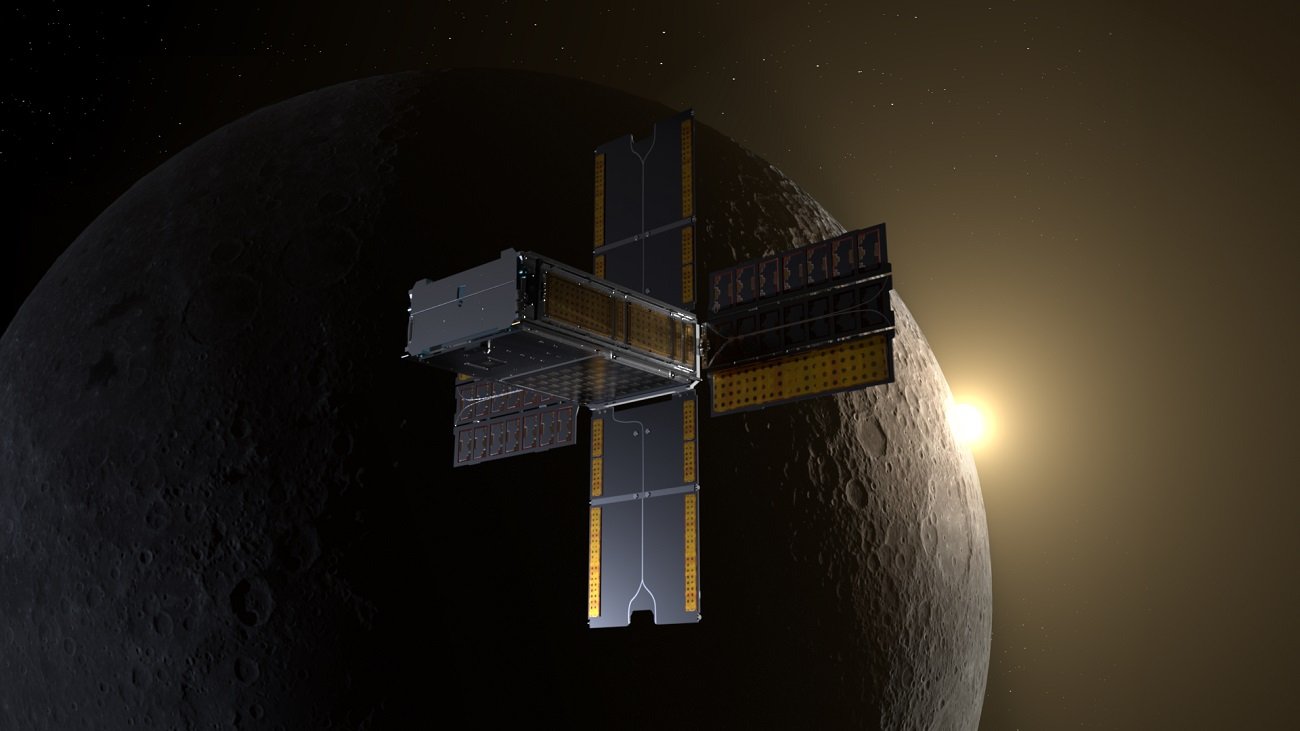
As part of the Biosentinel mission, NASA intends to place living creatures in space that will be farther from Earth than ever before.
This project will be carried out aboard the Artemis I lunar mission. The basis for these activities will be the heavy carrier rocket SLS (Space Launch System), the launch date of which is set for August 29.
Read also: The new Russian space station ROSS has been introduced, and we know its plan very well
Biosentinel will be carried out aboard the Orion spacecraft, traveling around the Moon and back to Earth. 10 CubeSats, i.e. small-sized satellites responsible for a number of scientific experiments, will also be launched. One of these devices would carry live yeast cells traveling in orbit around the sun. Sensors inside will allow scientists to study how cosmic rays affect living cells as they travel through outer space.
To date, missions into outer space have not only been deprived of all life – they have been deliberately removed so as not to lead to biological contamination of extraterrestrial objects. Of course, there were exceptions, like the Beresheet mission, which crashed into the moon’s surface, scattering terrestrial life forms known as tardigrades.
Since yeast cells show a striking resemblance to living cells in the human body, they should be an excellent predictor of the impact of cosmic rays and other factors on the health of astronauts. Both have similar biological mechanisms, including damage and repair. In both cases, genetic information is also carried in double-stranded DNA.
Earth’s magnetic field protects us from cosmic radiation, so potential missions to the Moon or Mars are unknown. How will people react to exposure to this radiation? Yeast aims to provide a preliminary answer to this question. By using an alternative to human cells, scientists plan to start looking for ways to mitigate the effects of exposure to cosmic rays.
Read also: Today, three asteroids disappeared from Earth by a hair! NASA said when will the next appear
First, the yeast charge will be placed inside the BioSentinel CubeSat. When the Artemis I mission makes its way to the Moon, the satellite will be deployed into a deep Earth orbit until it is beyond the range of our planet’s magnetic field. This is also when the actual part of the 12-month assignment will begin. Two other experiments are also planned: aboard the International Space Station and on Earth. Scientists will use the data collected to plan missions targeting the Red Planet.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.