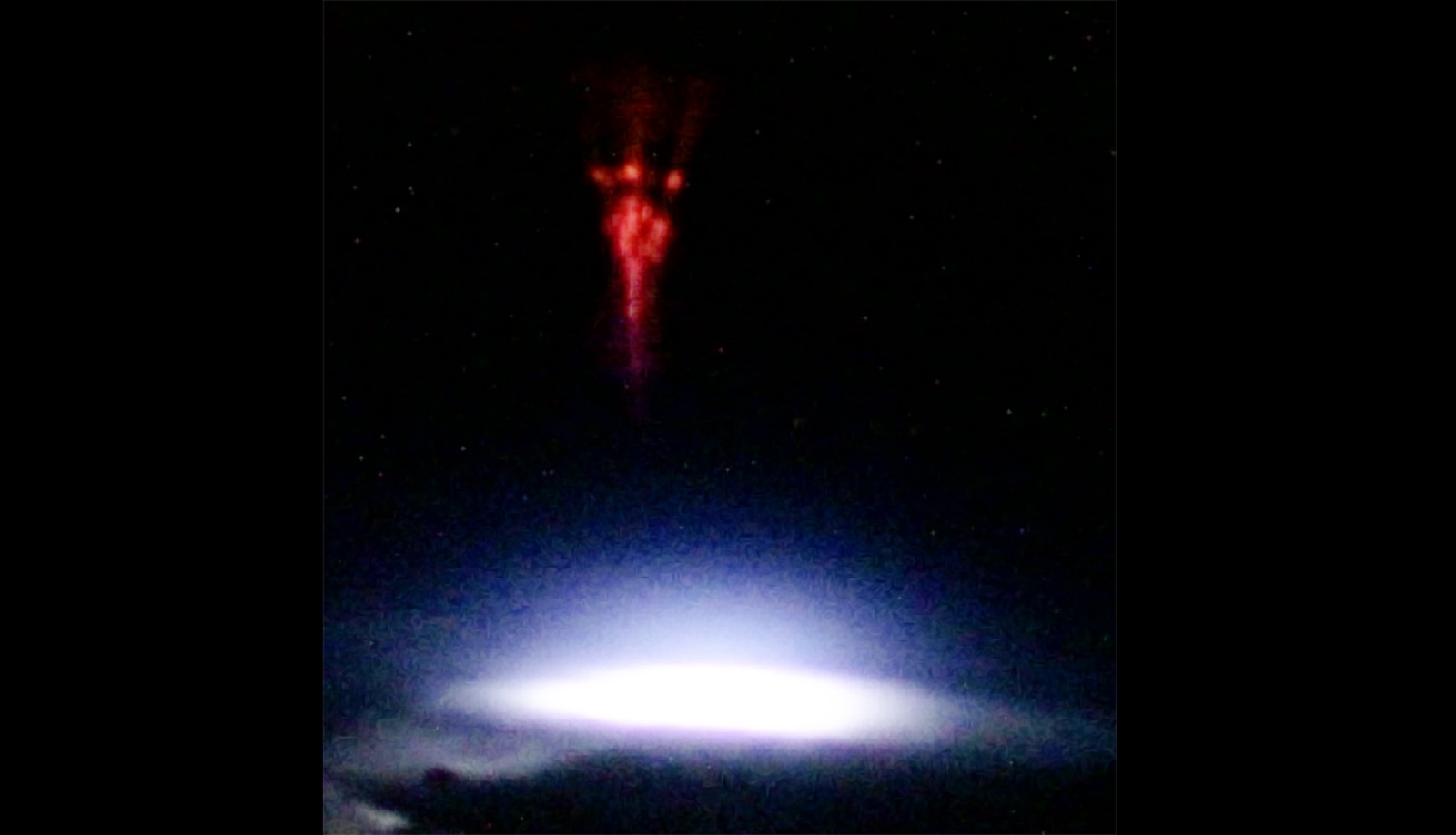
These, sometimes called goblins or fairies, are created as a result of atmospheric phenomena that occur in the ionosphere. It is a type of very strong electrical discharge, and although it occurs at very high altitudes, it may be the result of discharges from clouds to the ground or from clouds to clouds.
Read also: This technology will help astronomers, doctors and manufacturers. What is vector adaptive optics?
Mogensen, who performs various tasks on the International Space Station, goes to the monitoring module every Saturday and monitors storms emerging from there. All this in order to learn as much as possible about the conditions under which severe storms and various types of weather phenomena occur at high altitudes.
The photo showing the red object known as the Sprite was taken by Andreas Mogensen, an astronaut aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
In such conditions, a red glow was captured, which is usually visible at an altitude of 40 to 80 kilometers. Goblin sightings have been reported in the past, thanks to pilots. The first confirmed detection was made in July 1989. The small number of such observations is due primarily to the fact that it is almost impossible to see these red sprites from the surface of our planet.
Read also: High school students and the International Space Station. This is how our planet’s magnetic field is measured
As a result, the best opportunity to make observations is provided by tracking from a higher altitude. The International Space Station, which orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 kilometers, is ideal for this role. The distinctive color of these discharges appears when the discharge meets the nitrogen present in the Earth’s atmosphere. The photo may not have been taken at all if it were not for the technological advances of the camera, which is capable of taking up to 100,000 images per second. Scientists typically use such an instrument to image lightning discharges in the upper atmosphere and study their effect on greenhouse gas concentrations.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.