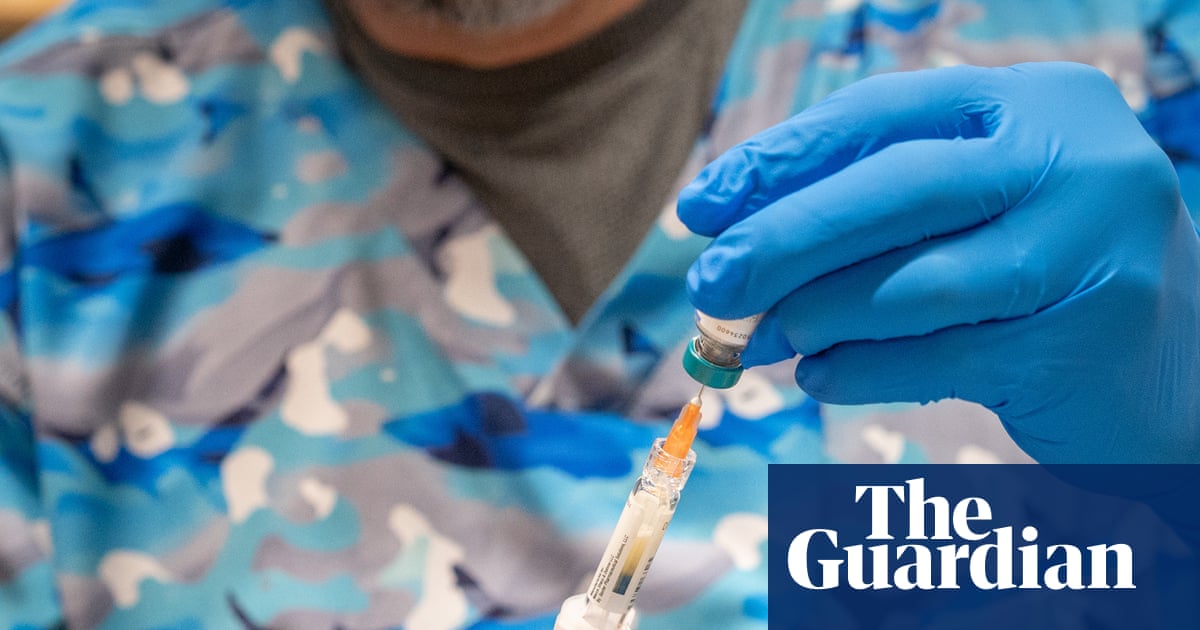
Five new consultants will join the vaccine for US Disease Control and Prevention Centers this weekend, announcing the agency and the US Health and Human […]
Prehistoric Amber is light on the ancient Amazon rainforest
Washington. Many models found in a sandstone quarry from Ecuador to 112 million years ago, Fabiani Herrera, co -editor of fossil plants at the Field […]
How Blockchain is Changing Sports Marketing
Blockchain is shaking up sports marketing. It boosts fan engagement, improves loyalty programs, and ensures more transparent sponsorships. It also helps verify the authenticity of […]
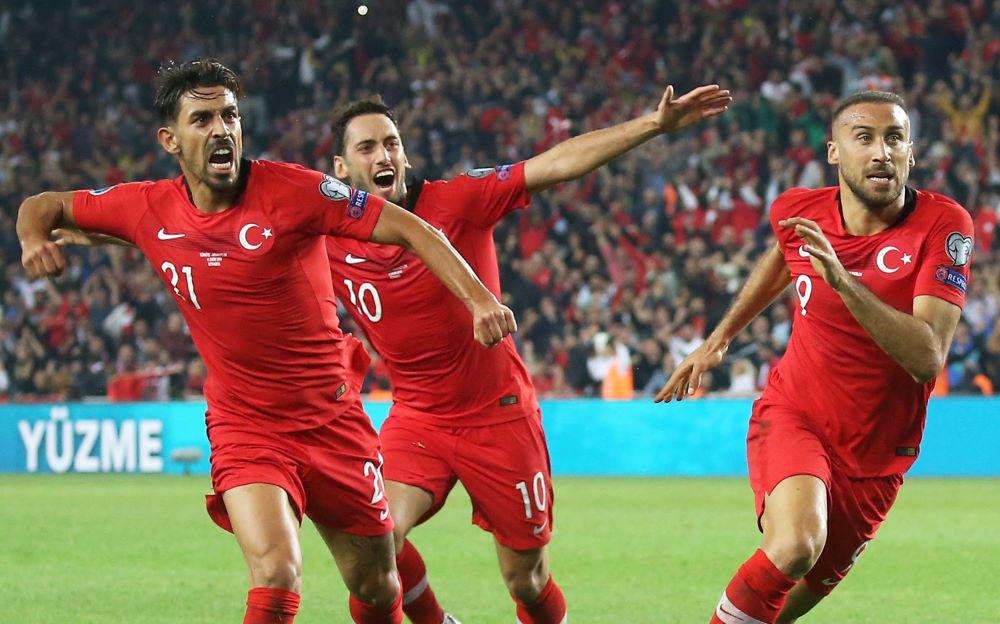
THE RISING GLOBAL POPULARITY OF THE TURKISH FOOTBALL LEAGUE
In recent years, the Turkish Süper Lig, Turkey’s top-tier football league, has gained significant traction on the international stage. This rise in popularity can be […]
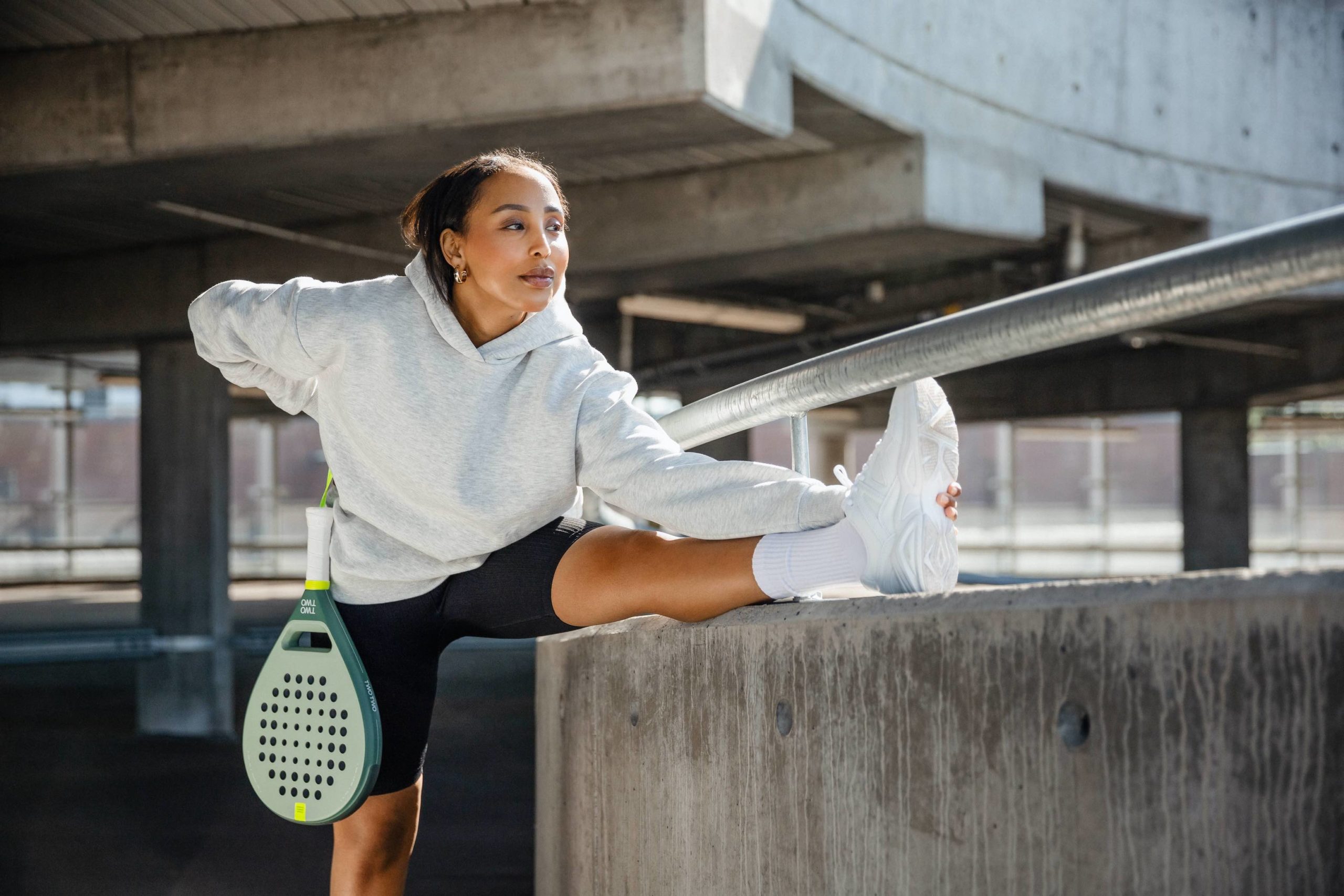
Padel: The Fast-Growing Sport Shaping the Future of Recreation
Padel is a growing sport. It combines tennis and squash and is enjoyed by people all over. Its popularity is rising quickly, and the future […]
Top 6 Movies for Luck Hunters
Who doesn’t want to try his luck? For some, this is just a way to have fun, but for those who bet Canada or go […]
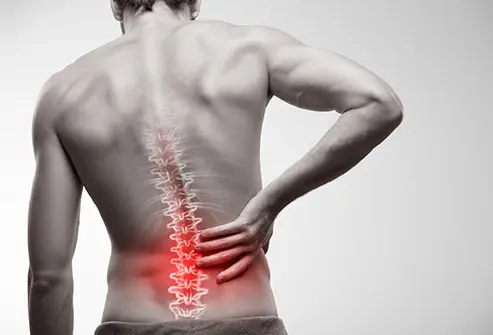
What to Do If Your Lower Back Hurts?
With lower back pain, every movement causes severe discomfort. A person cannot walk or even sit normally, his life turns into real torture. What causes […]
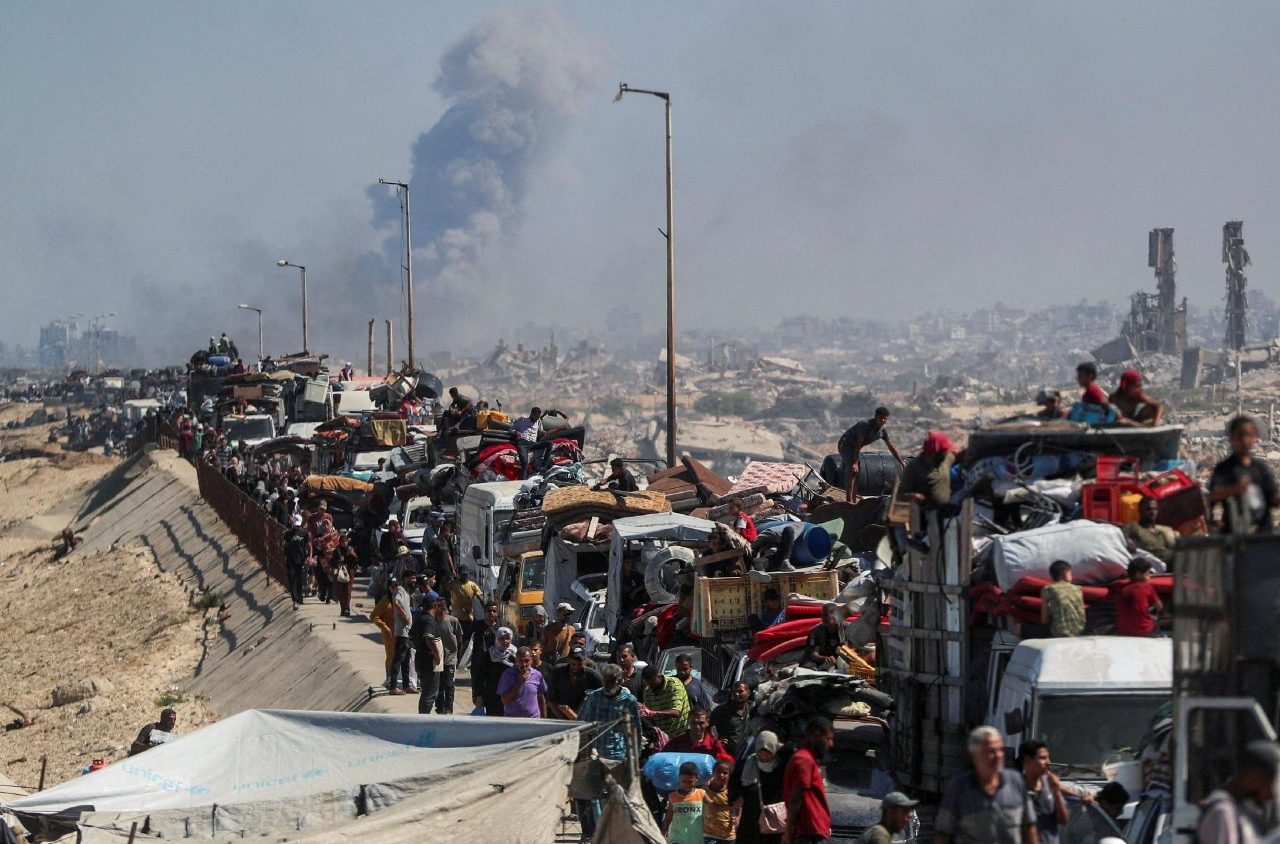
Bob renews an appeal for the ceasefire in Gaza: The dignity of a person who is not applicable to all must be respected
At the end of his weekly public audience, Pope Liu fourteen expresses his “deeper” sympathy for the people of Gaza. He renews his call for […]
Who was Celestay Rivas, who was found dead in Tesse of the missing teenage singer D4 VT? | Criminal messages
Lampman Lapd identified a woman’s body in the car of the romantic assassination singer T4 VT. In 2024, he disappeared at the age of 13. […]
Madonna reveals the upcoming new dance album next year, Warner Records Return
Madonna comes back into the ditch. Bob Queen on Thursday revealed that he was releasing a new dance album in 2026, and two decades after […]